2024网鼎杯[青龙组初赛]
Crypto
CRYPTO01
wdflag{39769372-2155-4c99-9ec2-6683c4451ed6}
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from secret import flag
p = getPrime(512)
q = getPrime(512)
n = p * q
d = getPrime(299)
e = inverse(d,(p-1)*(q-1))
m = bytes_to_long(flag)
c = pow(m,e,n)
hint1 = p >> (512-70)
hint2 = q >> (512-70)
print(f"n = {n}")
print(f"e = {e}")
print(f"c = {c}")
print(f"hint1 = {hint1}")
print(f"hint2 = {hint2}")
n =
e =
c =
hint1 = 954676601865566077628
hint2 = 5992567951560462279922023领航杯原题...说是boneh_durfee攻击
参考论文:https://eprint.iacr.org/2023/367.pdf
exp
import time
time.clock = time.time
debug = True
strict = False
helpful_only = True
dimension_min = 7 # 如果晶格达到该尺寸,则停止移除
# 显示有用矢量的统计数据
def helpful_vectors(BB, modulus):
nothelpful = 0
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
if BB[ii,ii] >= modulus:
nothelpful += 1
#print (nothelpful, "/", BB.dimensions()[0], " vectors are not helpful")
# 显示带有 0 和 X 的矩阵
def matrix_overview(BB, bound):
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
a = ('%02d ' % ii)
for jj in range(BB.dimensions()[1]):
a += '0' if BB[ii,jj] == 0 else 'X'
if BB.dimensions()[0] < 60:
a += ' '
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
a += '~'
#print (a)
# 尝试删除无用的向量
# 从当前 = n-1(最后一个向量)开始
def remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, current):
# 我们从当前 = n-1(最后一个向量)开始
if current == -1 or BB.dimensions()[0] <= dimension_min:
return BB
# 开始从后面检查
for ii in range(current, -1, -1):
# 如果它没有用
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
affected_vectors = 0
affected_vector_index = 0
# 让我们检查它是否影响其他向量
for jj in range(ii + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# 如果另一个向量受到影响:
# 我们增加计数
if BB[jj, ii] != 0:
affected_vectors += 1
affected_vector_index = jj
# 等级:0
# 如果没有其他载体最终受到影响
# 我们删除它
if affected_vectors == 0:
#print ("* removing unhelpful vector", ii)
BB = BB.delete_columns([ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([ii])
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii-1)
return BB
# 等级:1
#如果只有一个受到影响,我们会检查
# 如果它正在影响别的向量
elif affected_vectors == 1:
affected_deeper = True
for kk in range(affected_vector_index + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# 如果它影响哪怕一个向量
# 我们放弃这个
if BB[kk, affected_vector_index] != 0:
affected_deeper = False
# 如果没有其他向量受到影响,则将其删除,并且
# 这个有用的向量不够有用
#与我们无用的相比
if affected_deeper and abs(bound - BB[affected_vector_index, affected_vector_index]) < abs(bound - BB[ii, ii]):
#print ("* removing unhelpful vectors", ii, "and", affected_vector_index)
BB = BB.delete_columns([affected_vector_index, ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([affected_vector_index, ii])
monomials.pop(affected_vector_index)
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii-1)
return BB
# nothing happened
return BB
"""
Returns:
* 0,0 if it fails
* -1,-1 如果 "strict=true",并且行列式不受约束
* x0,y0 the solutions of `pol`
"""
def boneh_durfee(pol, modulus, mm, tt, XX, YY):
"""
Boneh and Durfee revisited by Herrmann and May
在以下情况下找到解决方案:
* d < N^delta
* |x|< e^delta
* |y|< e^0.5
每当 delta < 1 - sqrt(2)/2 ~ 0.292
"""
# substitution (Herrman and May)
PR.<u, x, y> = PolynomialRing(ZZ) #多项式环
Q = PR.quotient(x*y + 1 - u) # u = xy + 1
polZ = Q(pol).lift()
UU = XX*YY + 1
# x-移位
gg = []
for kk in range(mm + 1):
for ii in range(mm - kk + 1):
xshift = x^ii * modulus^(mm - kk) * polZ(u, x, y)^kk
gg.append(xshift)
gg.sort()
# 单项式 x 移位列表
monomials = []
for polynomial in gg:
for monomial in polynomial.monomials(): #对于多项式中的单项式。单项式():
if monomial not in monomials: # 如果单项不在单项中
monomials.append(monomial)
monomials.sort()
# y-移位
for jj in range(1, tt + 1):
for kk in range(floor(mm/tt) * jj, mm + 1):
yshift = y^jj * polZ(u, x, y)^kk * modulus^(mm - kk)
yshift = Q(yshift).lift()
gg.append(yshift) # substitution
# 单项式 y 移位列表
for jj in range(1, tt + 1):
for kk in range(floor(mm/tt) * jj, mm + 1):
monomials.append(u^kk * y^jj)
# 构造格 B
nn = len(monomials)
BB = Matrix(ZZ, nn)
for ii in range(nn):
BB[ii, 0] = gg[ii](0, 0, 0)
for jj in range(1, ii + 1):
if monomials[jj] in gg[ii].monomials():
BB[ii, jj] = gg[ii].monomial_coefficient(monomials[jj]) * monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
#约化格的原型
if helpful_only:
# #自动删除
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, modulus^mm, nn-1)
# 重置维度
nn = BB.dimensions()[0]
if nn == 0:
print ("failure")
return 0,0
# 检查向量是否有帮助
if debug:
helpful_vectors(BB, modulus^mm)
# 检查行列式是否正确界定
det = BB.det()
bound = modulus^(mm*nn)
if det >= bound:
print ("We do not have det < bound. Solutions might not be found.")
print ("Try with highers m and t.")
if debug:
diff = (log(det) - log(bound)) / log(2)
print ("size det(L) - size e^(m*n) = ", floor(diff))
if strict:
return -1, -1
else:
print ("det(L) < e^(m*n) (good! If a solution exists < N^delta, it will be found)")
# display the lattice basis
if debug:
matrix_overview(BB, modulus^mm)
# LLL
if debug:
print ("optimizing basis of the lattice via LLL, this can take a long time")
#BB = BB.BKZ(block_size=25)
BB = BB.LLL()
if debug:
print ("LLL is done!")
# 替换向量 i 和 j ->多项式 1 和 2
if debug:
print ("在格中寻找线性无关向量")
found_polynomials = False
for pol1_idx in range(nn - 1):
for pol2_idx in range(pol1_idx + 1, nn):
# 对于i and j, 构造两个多项式
PR.<w,z> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
pol1 = pol2 = 0
for jj in range(nn):
pol1 += monomials[jj](w*z+1,w,z) * BB[pol1_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
pol2 += monomials[jj](w*z+1,w,z) * BB[pol2_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
# 结果
PR.<q> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
rr = pol1.resultant(pol2)
if rr.is_zero() or rr.monomials() == [1]:
continue
else:
print ("found them, using vectors", pol1_idx, "and", pol2_idx)
found_polynomials = True
break
if found_polynomials:
break
if not found_polynomials:
print ("no independant vectors could be found. This should very rarely happen...")
return 0, 0
rr = rr(q, q)
# solutions
soly = rr.roots()
if len(soly) == 0:
print ("Your prediction (delta) is too small")
return 0, 0
soly = soly[0][0]
ss = pol1(q, soly)
solx = ss.roots()[0][0]
return solx, soly
def example():
############################################
# 随机生成数据
##########################################
#start_time =time.perf_counter
start =time.clock()
size=512
length_N = 2*size;
ss=0
s=70;
M=1 # the number of experiments
delta = 299/1024
# p = random_prime(2^512,2^511)
for i in range(M):
# p = random_prime(2^size,None,2^(size-1))
# q = random_prime(2^size,None,2^(size-1))
# if(p<q):
# temp=p
# p=q
# q=temp
N =
e =
c =
hint1 =
hint2 =
# print ("p真实高",s,"比特:", int(p/2^(512-s)))
# print ("q真实高",s,"比特:", int(q/2^(512-s)))
# N = p*q;
# 解密指数d的指数( 最大0.292)
m = 7 # 格大小(越大越好/越慢)
t = round(((1-2*delta) * m)) # 来自 Herrmann 和 May 的优化
X = floor(N^delta) #
Y = floor(N^(1/2)/2^s) # 如果 p、 q 大小相同,则正确
for l in range(int(hint1),int(hint1)+1):
print('\n\n\n l=',l)
pM=l;
p0=pM*2^(size-s)+2^(size-s)-1;
q0=N/p0;
qM=int(q0/2^(size-s))
A = N + 1-pM*2^(size-s)-qM*2^(size-s);
#A = N+1
P.<x,y> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
pol = 1 + x * (A + y) #构建的方程
# Checking bounds
#if debug:
#print ("=== 核对数据 ===")
#print ("* delta:", delta)
#print ("* delta < 0.292", delta < 0.292)
#print ("* size of e:", ceil(log(e)/log(2))) # e的bit数
# print ("* size of N:", len(bin(N))) # N的bit数
#print ("* size of N:", ceil(log(N)/log(2))) # N的bit数
#print ("* m:", m, ", t:", t)
# boneh_durfee
if debug:
##print ("=== running algorithm ===")
start_time = time.time()
solx, soly = boneh_durfee(pol, e, m, t, X, Y)
if solx > 0:
#print ("=== solution found ===")
if False:
print ("x:", solx)
print ("y:", soly)
d_sol = int(pol(solx, soly) / e)
ss=ss+1
print ("=== solution found ===")
print ("p的高比特为:",l)
print ("q的高比特为:",qM)
print ("d=",d_sol)
if debug:
print("=== %s seconds ===" % (time.time() - start_time))
#break
print("ss=",ss)
#end=time.process_time
end=time.clock()
print('Running time: %s Seconds'%(end-start))
if __name__ == "__main__":
example() 运行结果:
l= 954676601865566077628
det(L) < e^(m*n) (good! If a solution exists < N^delta, it will be found)
optimizing basis of the lattice via LLL, this can take a long time
LLL is done!
在格中寻找线性无关向量
found them, using vectors 0 and 1
=== solution found ===
p的高比特为: 954676601865566077628
q的高比特为: 599256795156046227991
d = 687038469975940863290260221773243585573217566356221334458982642899243861704377289553340363
=== 24.996796131134033 seconds ===
ss= 1
Running time: 25.003862619400024 Seconds获得了d,常规RSA解密就能获得flag了
wdflag{39769372-2155-4c99-9ec2-6683c4451ed6}
CRYPTO02
wdflag{6d0aea686e480cf0ea9143b85a42a046}
import gmpy2
import random
import binascii
from hashlib import sha256
from sympy import nextprime
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
def victory_encrypt(plaintext, key):
key = key.upper()
key_length = len(key)
plaintext = plaintext.upper()
ciphertext = ''
for i, char in enumerate(plaintext):
if char.isalpha():
shift = ord(key[i % key_length]) - ord('A')
encrypted_char = chr((ord(char) - ord('A') + shift) % 26 + ord('A'))
ciphertext += encrypted_char
else:
ciphertext += char
return ciphertext
victory_key = "WANGDINGCUP"
victory_encrypted_flag = victory_encrypt(flag, victory_key)
p = 0xfffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffefffffc2f
a = 0
b = 7
xG = 0x79be667ef9dcbbac55a06295ce870b07029bfcdb2dce28d959f2815b16f81798
yG = 0x483ada7726a3c4655da4fbfc0e1108a8fd17b448a68554199c47d08ffb10d4b8
G = (xG, yG)
n = 0xfffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffebaaedce6af48a03bbfd25e8cd0364141
h = 1
zero = (0,0)
dA = nextprime(random.randint(0, n))
if dA > n:
print("warning!!")
def addition(t1, t2):
if t1 == zero:
return t2
if t2 == zero:
return t2
(m1, n1) = t1
(m2, n2) = t2
if m1 == m2:
if n1 == 0 or n1 != n2:
return zero
else:
k = (3 * m1 * m1 + a) % p * gmpy2.invert(2 * n1 , p) % p
else:
k = (n2 - n1 + p) % p * gmpy2.invert((m2 - m1 + p) % p, p) % p
m3 = (k * k % p - m1 - m2 + p * 2) % p
n3 = (k * (m1 - m3) % p - n1 + p) % p
return (int(m3),int(n3))
def multiplication(x, k):
ans = zero
t = 1
while(t <= k):
if (k &t )>0:
ans = addition(ans, x)
x = addition(x, x)
t <<= 1
return ans
def getrs(z, k):
(xp, yp) = P
r = xp
s = (z + r * dA % n) % n * gmpy2.invert(k, n) % n
return r,s
z1 = random.randint(0, p)
z2 = random.randint(0, p)
k = random.randint(0, n)
P = multiplication(G, k)
hA = multiplication(G, dA)
r1, s1 = getrs(z1, k)
r2, s2 = getrs(z2, k)
print("r1 = {}".format(r1))
print("r2 = {}".format(r2))
print("s1 = {}".format(s1))
print("s2 = {}".format(s2))
print("z1 = {}".format(z1))
print("z2 = {}".format(z2))
key = sha256(long_to_bytes(dA)).digest()
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC)
iv = cipher.iv
encrypted_flag = cipher.encrypt(pad(victory_encrypted_flag.encode(), AES.block_size))
encrypted_flag_hex = binascii.hexlify(iv + encrypted_flag).decode('utf-8')
print("Encrypted flag (AES in CBC mode, hex):", encrypted_flag_hex)分析源代码,知道flag先进行了维吉尼亚加密,再AES加密,且输出的密文是IV+flag密文
def getrs(z, k):
(xp, yp) = P
r = xp
s = (z + r * dA % n) % n * gmpy2.invert(k, n) % n
return r,s
z1 = random.randint(0, p)
z2 = random.randint(0, p)
k = random.randint(0, n)
P = multiplication(G, k)
hA = multiplication(G, dA)
r1, s1 = getrs(z1, k)
r2, s2 = getrs(z2, k)根据这段代码知道可以通过 s1,s2 来求 k 的逆元,再通过 z1,z2 来求 k
获得 k 以后可以用来求 dA
import gmpy2
k1 = gmpy2.invert(s1-s2, n)
k = ((z1 - z2) * k1) % n
r1 = gmpy2.invert(r1, n)
dA = ((s1 * k - z1) * r1) % n拿到dA后就能获取到key了
import binascii
from hashlib import sha256
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import unpad
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
key = sha256(long_to_bytes(dA)).digest()
cipte="输出的密文"
encrypted_flag = binascii.unhexlify(cipte)
#前16位是iv,去掉iv后才是真密文
iv = encrypted_flag[:16]
encrypted_flag_1 = encrypted_flag[16:]
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)
decrypted_flag = unpad(cipher.decrypt(encrypted_flag_1),AES.block_size)执行后获得SDSRDO{6F0PAA686M480WU0EN9143H85P42N046}
源码中有维吉尼亚的加密函数和密钥
def victory_encrypt(plaintext, key):
key = key.upper()
key_length = len(key)
plaintext = plaintext.upper()
ciphertext = ''
for i, char in enumerate(plaintext):
if char.isalpha():
shift = ord(key[i % key_length]) - ord('A')
encrypted_char = chr((ord(char) - ord('A') + shift) % 26 + ord('A'))
ciphertext += encrypted_char
else:
ciphertext += char
return ciphertext将其中的+ shift改成- shift就是解密函数,利用密钥直接进行解密就行,解密的结果要改成小写
wdflag{6d0aea686e480cf0ea9143b85a42a046}
Misc
MISC03
wdflag{39.168.5.60}
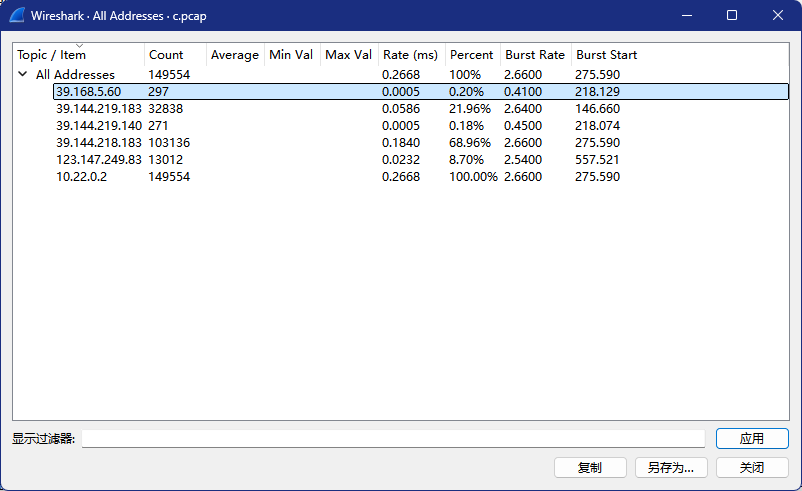
Wireshark的统计功能,统计出这几个ip,一个个试,发现攻击者ip是39.168.5.60
MISC04
wdflag{3f531c43-3b8b-42ab-babf-567f1216fa06}
希尔伯特-皮亚诺曲线
exp
from PIL import Image
from tqdm import tqdm
def peano(n):
if n == 0:
return [[0,0]]
else:
in_lst = peano(n - 1)
lst = in_lst.copy()
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px - i[0], py + 1 + i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px + i[0], py + 1 + i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px + 1 + i[0], py - i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px - i[0], py - 1 - i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px + i[0], py - 1 - i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px + 1 + i[0], py + i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px - i[0], py + 1 + i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px + i[0], py + 1 + i[1]] for i in in_lst)
return lst
order = peano(6)
img = Image.open("1.png")
width, height = img.size
block_width = width # // 3
block_height = height # // 3
new_image = Image.new("RGB", (width, height))
for i, (x, y) in tqdm(enumerate(order)):
# 根据列表顺序获取新的坐标
new_x, new_y = i % width, i // width
# 获取原图像素
pixel = img.getpixel((x, height - 1 - y))
# 在新图像中放置像素
new_image.putpixel((new_x, new_y), pixel)
new_image.save("rearranged_image.jpg")还原后的图片是一张二维码
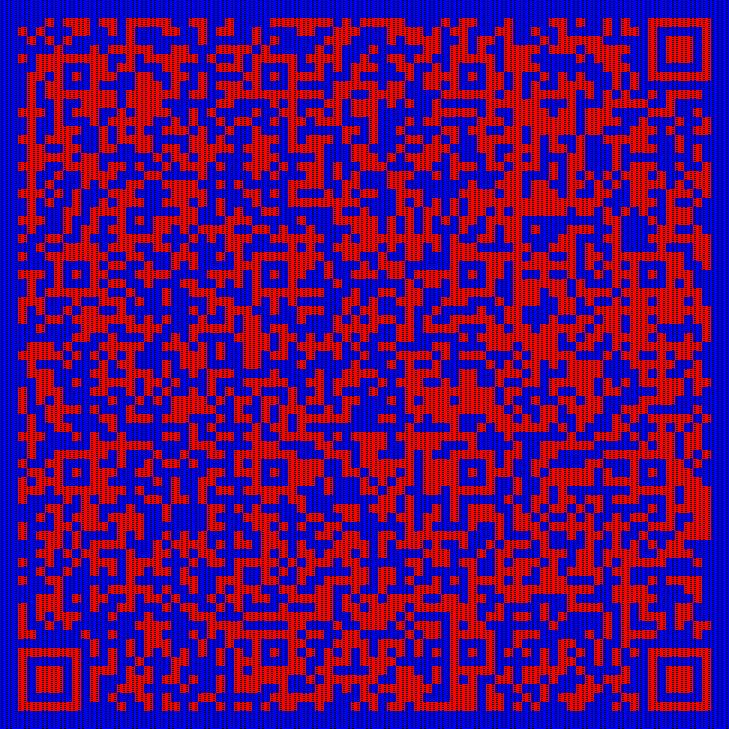
扫码获得:wdflag{3f531c43-3b8b-42ab-babf-567f1216fa06}
Reverse
REVERSE02
wdflag{9e855bae8f9aaafe9a2eb2cbd8823519}

将flag分成了四个部分,逐一解密

第一部分,就是将用户输入的前八位*2和s2对比,所以将s2/2就行了
s2 =[0x72,0xCA,0x70,0x6A,0x6A,0xC4,0xC2,0xCA]
for i in s2:
print(chr(i//2),end="")获得9e855bae
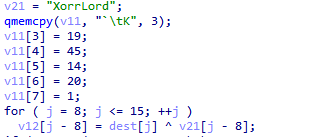
第二部分,v11进行了异或操作,key是v21
v11 = ["`","\t","K",chr(19),chr(45),chr(14),chr(20),chr(1)]
key = "XorrLord"
for i in range(8):
print(chr(ord(v11[i])^ord(key[i])),end="")获得8f9aaafe

第三部分,base64编码,不过换了码表

码表不要忘了加C,CDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/
密文是QYGyBYKyA2K
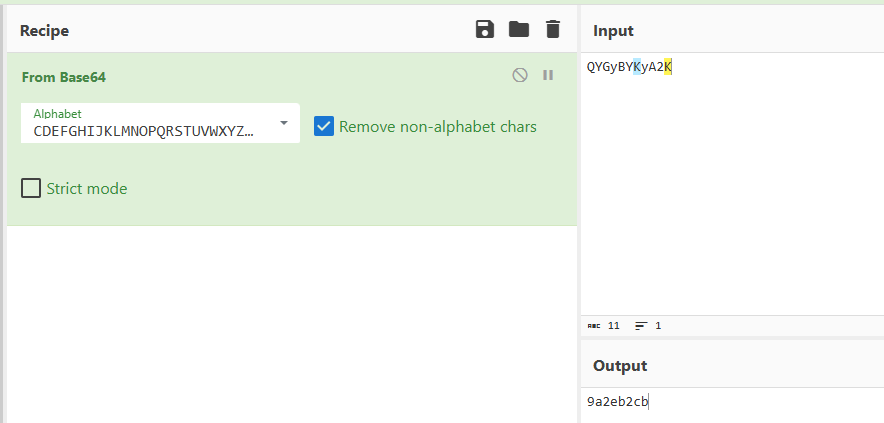
解密获得:9a2eb2cb
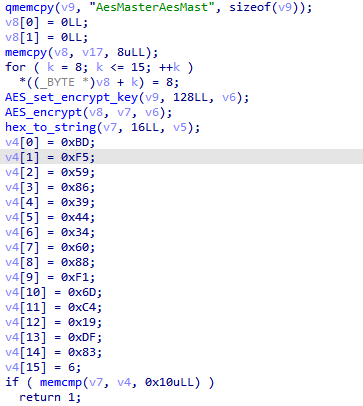
第四部分,就是AES加密,密钥就是v9,密文就是v4
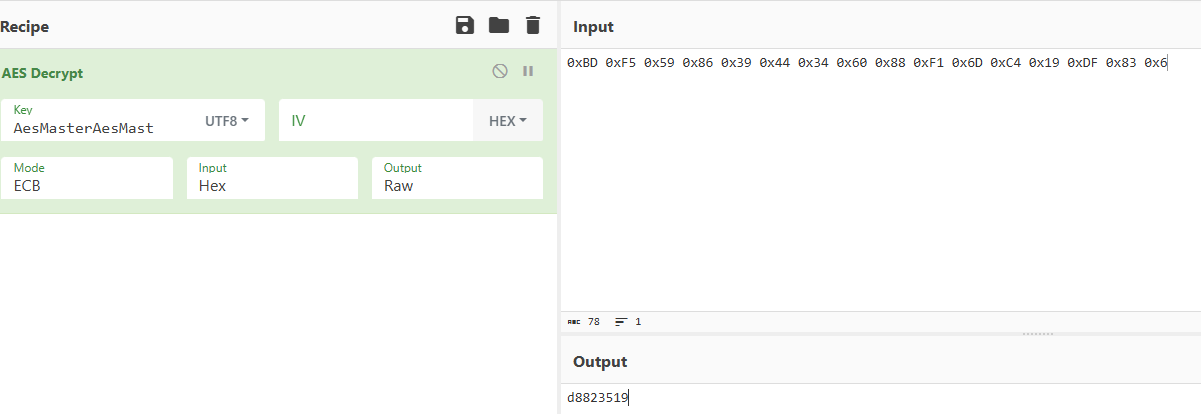
解密获得:d8823519
将四个flag拼在一起就是flag
wdflag{9e855bae8f9aaafe9a2eb2cbd8823519}